
Does TV Resolution Matter? [Video]
Video uploaded by BrainStuff – HowStuffWorks on February 23, 2016
Contents
UHD, OLED, HDR: What Do All These Abbreviations Stand for in Television
It tends to happen often, whenever we buy a new TV. We open up the manual and read a bunch of abbreviations we don’t understand, and get overwhelmed. Then we also start to wonder about the product itself and all its features and if we made the right decision in choosing the right TV based on price and features altogether. We are going to tell you a little bit about the television market and products, and hopefully ease some of those worries for you with some words of advice.
Choosing a TV in the past was simple. We would enter a television showroom of any electronic store, and it was never a big deal making a decision on which television to buy. Options were simple, there were either a few tube televisions, or several narrow flat plasma-panels. Today, there is such a diversity that it is almost impossible to buy a television easily anymore. Advertisements mention things like UHDTV, HDR, QLED, and we don’t understand a word they are saying.
Screen Producing Technologies
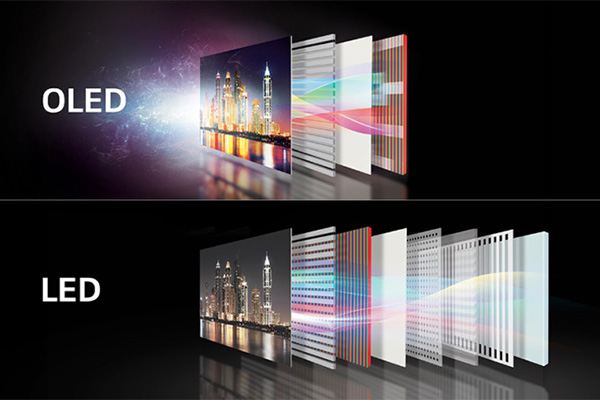
The most recognized technologies in screen producing business today is LED, OLED and QLED. All of them refer to light emitting diodes (LED), that any modern screen would be built of. Diodes have already proven themselves safe, efficient, and less expensive in terms of light. So what are the difference between the LED, OLED, QLED names, if they are still the same diodes in every screen?
LCD
Liquid crystal displays are most common in term of screens, everywhere. They are made of liquid crystals that are used for major screen types. Those elements don’t produce light, so modern TV screens are constructed with a led-backgrounder. The main benefit is in the weakest pixel degradation that offers long term using. Depending on the way LCD-screens were created, these screens can have big angle views together with high quality pictures. Another plus is they are not expensive.

Liquid-crystal-display television (LCD TV) from Samsung
OLED
OLED based screens consist of organic diodes. n organic-polymer membrane organized in layers, is how this technology gets its name. Such TVs will attract you with higher brightness level and color saturation opposed to traditional LED back lightened panels. OLED panels are the only ones that have a wide brightness range with true black color. Viewing angles are also slightly improved. OLED screens have less energy consumption and a thinner body (due to lack of the backlight layer). The price on the other hand, is also higher. Organic diodes also tend to have less life time opposed to traditional diodes.

OLED television from Philips
QLED
QLED is a modern technology originally developed by Samsung Electronics. Despite the name, the construction of the screen is closer to the simple LED rather than the OLED. “Quantum dot” is the name of a very small crystal that is a pixel in QLED screens. Those crystals begin to glow brightly with colors when currently running through the screen-matrix. QLED panels archive wider color ranges between any other panels and have minimum energy consumption. Besides, QLED panels have a 7-year life time, way beyond the OLED.
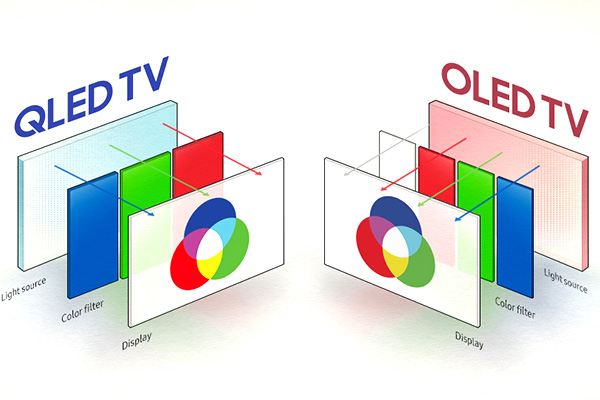
QLED technology
Picture Enhancement Technologies
Among all the hardware engineering there is also a major software side of the “best looking picture” aspect in the television screens. One of them is the HDR (High Dynamic Range) technology.
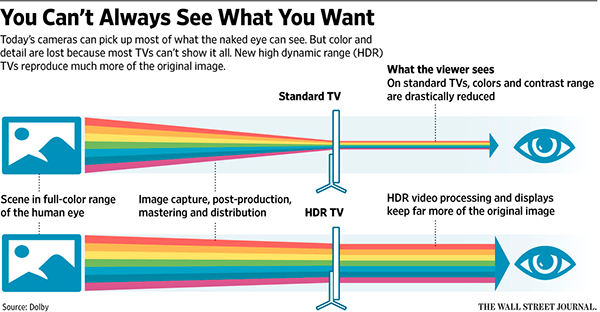
Picture enhancement technologies: how it works
HDR10
The HDR10 standard, supported by devices marked with Premium UHD logo, offers a 10-bit color depth. That means you will be able to see details in night scenes but not in just all-black pictures. Such software improvements are also used in video-gaming to boost the ambiance of the game.

HDR10: how it works
HDR Dolby Vision
This version of the HDR standard produces the best HDR effect today and supports a 12-bit color depth. The TV will need an additional hardware chip to process the 12-bit color depth picture. This will affect the price range of TV models with HDR Dolby Vision but you will get outstanding picture quality in return.

HDR Dolby Vision technology
HDR10+
Introduced by Samsung, this color enhancing algorithm can separately compute contrast ratio and depth of color for every single scene in real time (HDR10 and HDR Dolby Vision both offer static scene computing). The main benefit of HDR10+is being able to enhance picture of stream-videos due to its wider dynamic color range. Today, the only service that supports HDR10+ is Amazon Video.

HDR10+ technology
Screen Resolution (pixels)
Now approach another tricky question – screen resolution. You should start from 4K and up if you are looking for a big size movie panel in the guest room. The old-fashioned Full HD resolution will be enough for a small sized screen in the kitchen.
UHD (or 4K)
UHD or 4K screen resolution is the most common, technological and advanced for nowadays’ flagship panels. It’s called 4K because it has 4 times more pixels compared to Full HD screens. As for the customer, it will be a difference in picture sharpness but the same diagonal size. The scene will also look smoother and more natural.
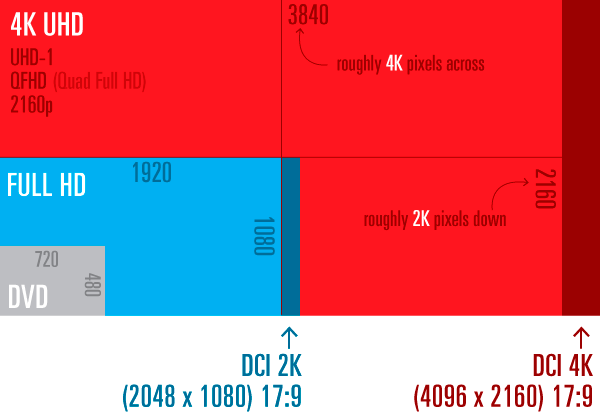
UHD (4K) resolution
SUHD
A Samsung marketing abbreviation for panels, based on quantum dots (or QLED as mentioned earlier). It has nothing in common with the Super UHD, it just means a 4K resolution, but in the QLED series of products.

SUHD resolution
8K UHD
No compromises, this is furthest advance in screen resolutions and means eight-fold Full HD increase. This standard in picture resolution will became common in a few years, but there are a few customer offers with 8K oday. A lack of 8K-recorded videos for the moment, marks those screens more “ahead of time” rather “practical necessity” nowadays.

8K UHD resolution
Links
- From 4K to UHD to 1080p: What you should know about TV resolutions – CNET
- Switching to a new TV model? Sell used Apple TV online for top dollar!
- Types of Smartphones’ Displays on the Market – iGotOffer





Facebook
Twitter
RSS